RudderStack's control plane provides a UI that lets you manage your source and destination configurations.
To self-host your source-destination configurations, you can use the open source Control Plane Lite utility to set up your own control plane. Control Plane Lite lets you manage your data pipelines locally by exporting or importing your configurations from a JSON file.
Setting up the control plane
Before setting up your self-hosted control plane, make sure you have installed Node.js.
To set up your self-hosted control plane using Control Plane Lite, follow these steps:
- Clone the RudderStack Control Plane Lite repository.
- Open your terminal and navigate to the Config Generator folder. Then, run the following commands:
npm installnpm start- After the setup is complete, you can access the dashboard at
http://localhost:3000by default.
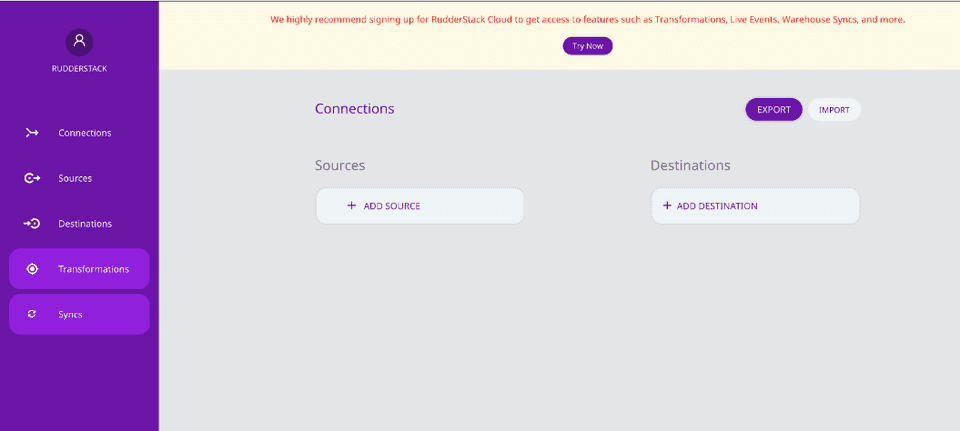
Exporting workspace configuration
After adding the required sources and destinations in the dashboard, you can export your workspace configuration by clicking the EXPORT button. The configuration is then exported and saved as a JSON file. This file is required to start the RudderStack server.
Starting RudderStack server with the workspace configuration file
For RudderStack to pick up the exported workspace configuration file, follow the steps in the below sections depending on your setup method.
Docker
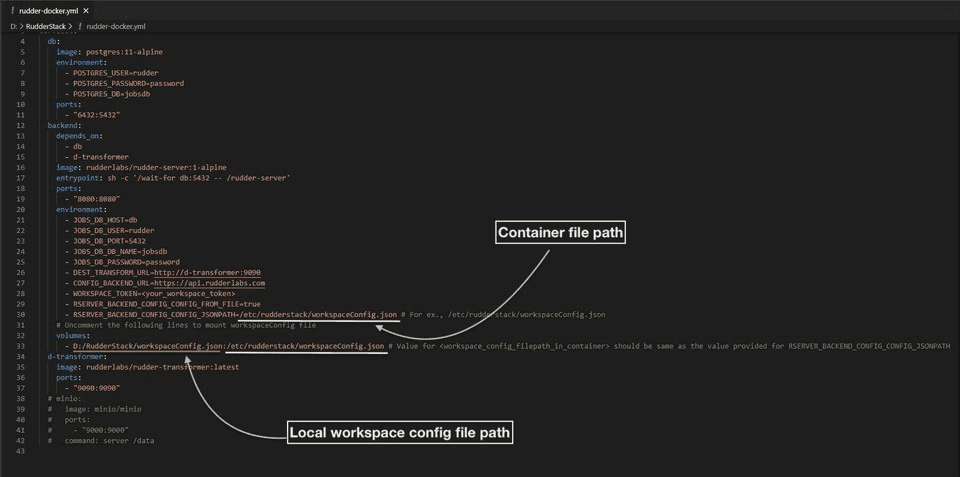
- Download and open
rudder-docker.yml. - In the
environmentsection underbackendservice, uncomment the following lines:
- RSERVER_BACKEND_CONFIG_CONFIG_FROM_FILE=true - RSERVER_BACKEND_CONFIG_CONFIG_JSONPATH=<workspace_config_filepath_in_container>- Then, replace
<workspace_config_filepath_in_container>in the above line with your container file path. By default, you can set it to/etc/rudderstack/workspaceConfig.json. - In the
volumessection under thebackendservice, uncomment the following line:
- <absolute_path_to_workspace_config>:<workspace_config_filepath_in_container>- Next, replace
<absolute_path_to_workspace_config>with the local path of yourworkspaceConfig.json(where your workspace configuration file is saved locally). Also, replace<workspace_config_filepath_in_container>with the container file path that you set in Step 3.
<workspace_config_filepath_in_container> should be the same as the value provided for the RSERVER_BACKEND_CONFIG_CONFIG_JSONPATH variable. Otherwise, your workspace configuration will not be loaded and you will get an error.- At this stage, your
rudder-docker.ymlshould look like the following:
- Finally, navigate to the directory where you want to install RudderStack and run the following command:
docker-compose -f rudder-docker.yml upOnce you have completed these steps above successfully, send test events to verify your installation.
Kubernetes
- Clone the repository containing the RudderStack Helm chart by running the following command:
git clone git@github.com:rudderlabs/rudderstack-helm.git- Navigate to the folder containing the Helm chart, as shown:
cd rudderstack-helm/- Open the
values.yamlfile. - Set the parameter
controlPlaneJSONtotrue. - Export the workspace configuration from the dashboard by following the steps in the Exporting workspace configuration section above. Place the exported file in the
rudderstack-helmfolder. - Finally, run the following command:
helm install my-release ./ --set backend.controlPlaneJSON=trueOnce you have completed these steps above successfully, send test events to verify your installation.
Developer machine setup
- First, set up the database in your preferred directory using the following commands:
createdb jobsdbcreateuser --superuser rudderpsql "jobsdb" -c "alter user rudder with encrypted password 'rudder'";psql "jobsdb" -c "grant all privileges on database jobsdb to rudder";- Next, clone the RudderStack server repository.
- Then, run
git submodule initandgit submodule updateto fetch therudder-transformerrepository. - Next, navigate to the rudder-transformer directory:
cd rudder-transformer- Install the dependencies using the command
npm i. Then, start the destination transformer using the following command:
node destTransformer.js- Navigate back to the main directory using the command
cd rudder-server. - Next, copy the
sample.envto the main directory, as shown:
cp config/sample.env .env- Then, go to the
configfolder and openconfig.yaml. - Under
[BackendConfig], look forconfigFromFileand set it totrue. - Also, change the value of
configJSONPathto the local path of yourworkspaceConfig.json(where your workspace configuration file is saved locally), as shown:
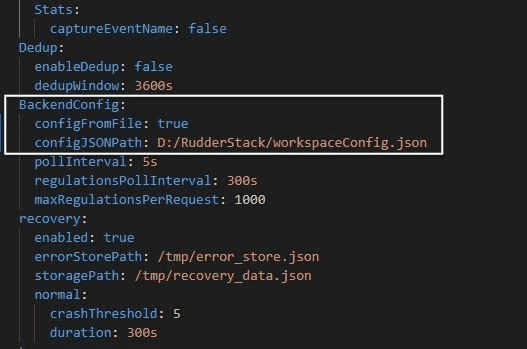
Finally, run the RudderStack server using the following command:
go run main.go
Once you have completed these steps above successfully, send test events to verify the installation.
Using SDK sources set up in self-hosted control plane
To use the RudderStack SDKs set up as sources in the self-hosted control plane, follow these steps:
- Set up the control plane using the Control Plane Lite utility.
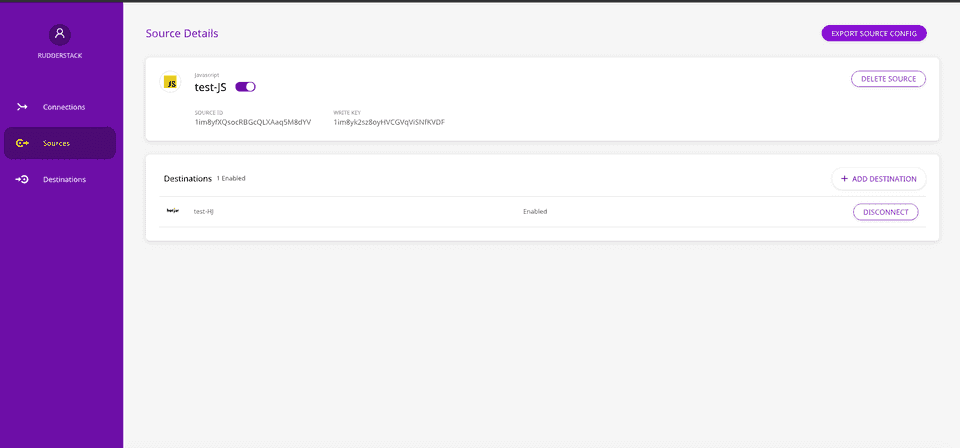
- Go to the dashboard, set up your source, and export the source configuration by clicking the EXPORT SOURCE CONFIG button, as shown:
- Host the exported file on your server such that it can be accessed via the path
<CONTROL_PLANE_URL>/sourceConfig. - Provide the base URL of your server (
<CONTROL_PLANE_URL>) serving this file in your SDK initialization code snippet. For more information on SDK initialization, refer to the following sections in the respective SDK guides:
- JavaScript SDK instructions
- Android SDK instructions
- iOS SDK instructions
- React Native SDK instructions
- Flutter SDK instructions
/sourceConfig to the base server URL provided above. For example, {CONTROL_PLANE_URL}/sourceConfig.A sample source configuration exported from the dashboard is shown below:
{ "source": { "config": {}, "id": "1im8yfXQsocRBGcQLXAaq5M8dYV", "name": "test-JS", "writeKey": "1im8yk2sz8oyHVCGVqViSNfKVDF", "enabled": true, "sourceDefinitionId": "1TW48i2bIzEl1HPf825cEznfIM8", "deleted": false, "createdAt": "Mon Oct 12 2020 16:51:54 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)", "updatedAt": "Mon Oct 12 2020 16:51:54 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)", "sourceDefinition": { "id": "1TW48i2bIzEl1HPf825cEznfIM8", "name": "JavaScript", "displayName": "JavaScript", "category": null, "createdAt": "2019-11-12T12:39:19.885Z", "updatedAt": "2020-06-18T11:54:06.114Z" }, }, "metadata": { "version": "1.0.2" }}Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.